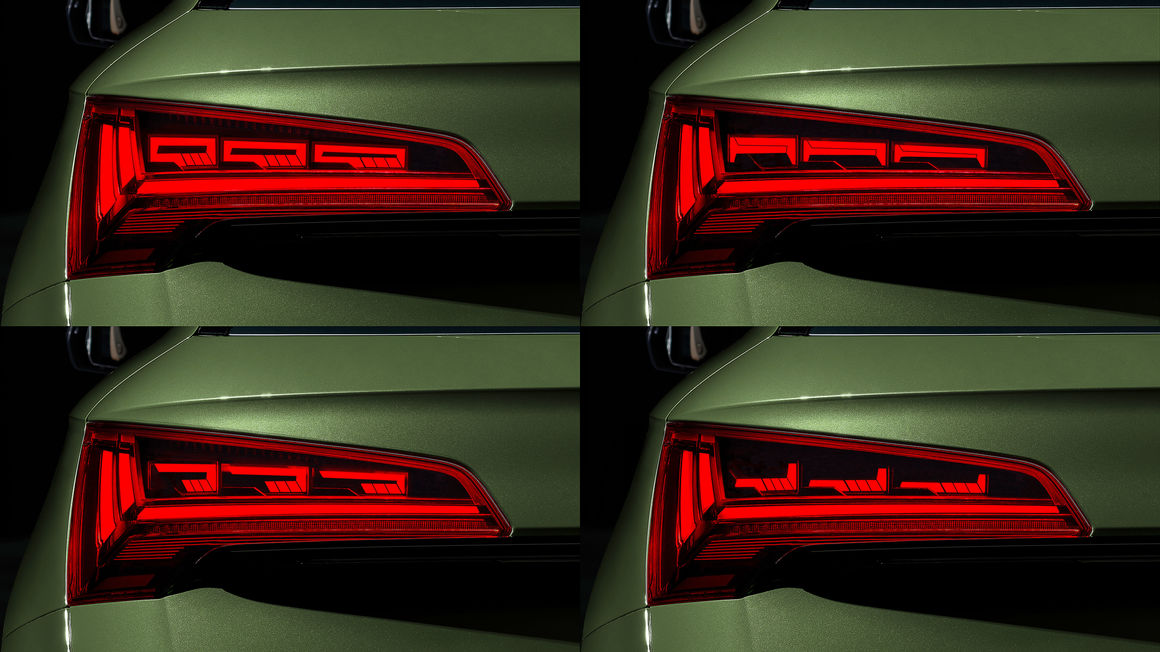
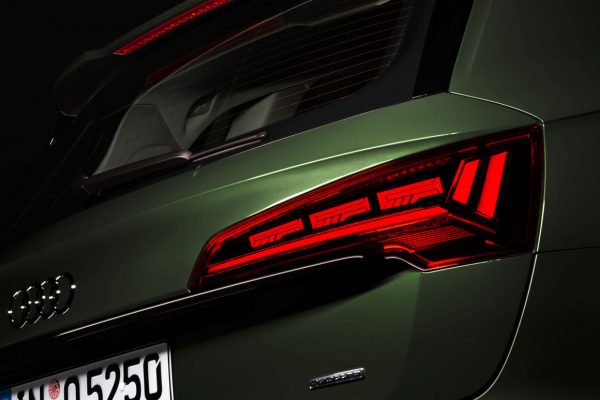
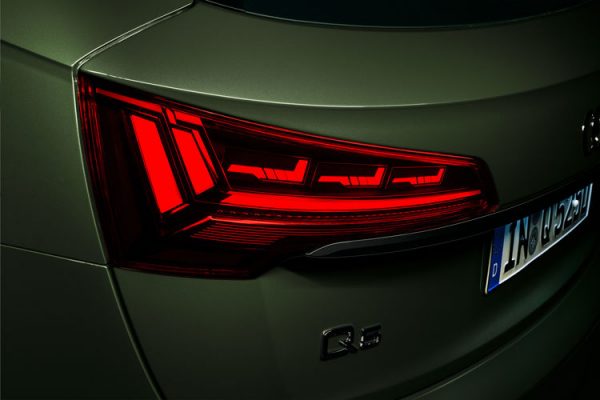
The facelifted Audi Q5 that was introduced last month boasts more than just a refreshed design. The SUV is now equipped with digital organic light-emitting diodes (OLED) taillights, something that have never been featured on an Audi before.
While OLEDs aren’t exactly new for the manufacturer, Audi’s digital OLED technology is revolutionary as it provides customisation and promotes safety, among other things.
For instance, buyers of the new Q5 are given the freedom to choose from three rear-light signatures and each signature has its own specific designs for coming and leaving home.
On the safety front, digital OLED comes with a proximity detection feature that will light up all the segments in the taillights when another road user approaches a stationary Q5 from the rear within less than two meters. How cool is that?

Learn more about Audi’s digital OLED taillights from the press release below:
PRESS RELEASE
In June 2020, the next generation of a lighting technology premiered in the Audi Q5: digital OLED technology. With organic light-emitting diodes (so-called OLEDs), Audi was a pioneer as far back as in 2016. Now digitalization is ringing in a new age. This technology promises to improve road safety and is the first to allow for personalization of the taillight signature.
Dr. Werner Thomas, OLED technology project manager at Audi, explains: “Headlight technology has seen a rapid evolution at Audi in recent decades. In addition, we have been decisively driving the development of rear-lighting systems.” The latest milestone achievement: now the brand is the first automobile manufacturer to digitize the taillights.
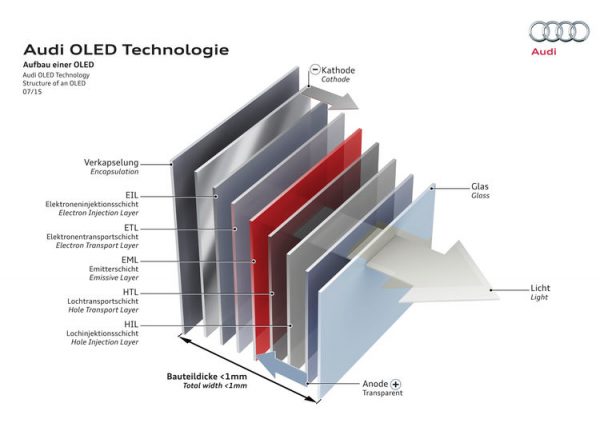
Why does Audi focus on OLED technology?
OLED light sources are panel radiators – unlike point light sources such as LEDs using semiconductor crystals. The benefits of OLEDs: Their light is extremely homogeneous. It is infinitely dimmable and achieves very high contrast. It can be split into segments. These segments are individually controllable and can develop diverse levels of brightness, with minimal gaps between the segments. The lighting unit does not require any reflectors, optical fibers or similar optics. This makes OLED units very efficient, lightweight and flat, which considerably increases design freedom.
An OLED lighting element is just one millimeter thin, while conventional LED solutions require much greater installed depths of 20 to 30 millimeters. The energy requirement of an OLED is once again significantly lower than that of LED optics if the latter are to achieve similar homogeneity. Audi’s OLED technology made its production debut in the taillight of the Audi TT RS1 in 2016. Up to now, Audi models using OLED lighting technology have had up to four individually controllable, complex lighting segments that could be used for an individual, defined lighting design.
What benefits do Audi’s new digital OLEDs offer?
The larger number of individually controllable segments can now be randomly activated, with continuous variability of brightness. In the Q5, three tiles of six units each, in other words 18 segments per lamp, are currently used. The high precision and great variability offer light designers a wealth of opportunities, using just one type of hardware. Q5 customers opting for digital OLED technology have a choice of three signatures in the taillights when purchasing their car. In the “dynamic” Audi drive select mode, the lamps additionally switch to another signature. Moreover, animation effects such as coming-home/leaving-home lighting scenarios can be implemented, plus the dynamic flashing light has been integrated in the new lamp units as well
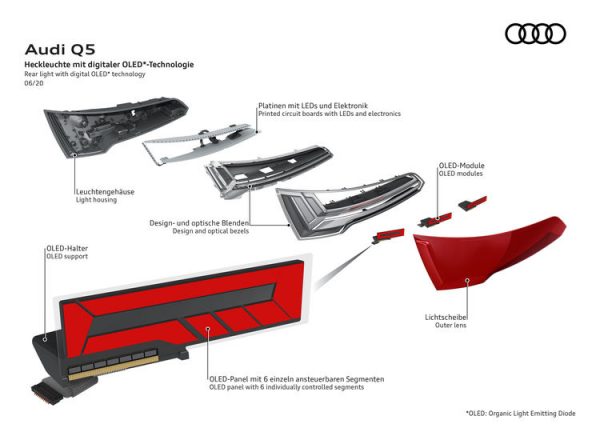

How exactly do digital OLEDs differ from established OLED technology?
“Up to now, we have been using OLED segmentation with the Audi TT RS1 and A8 for designing signature lighting. This has changed with the Q5,” says OLED technology project manager Dr. Werner Thomas. “Here the taillights turn into a kind of display on the outer shell, which will provide us with ample opportunities and prospects in terms of design, personalization, communication and safety going forward.” Thus, the year 2020 marks the threshold of a new age: a pure medium for signal functions is now additionally becoming a medium for displaying diverse types of content.
How do digital OLED lamps improve road safety?
In the new Q5, Audi has implemented a proximity detection feature for the versions using digital OLED taillights. When another road user approaches a stationary Q5 from the rear within less than two meters, all the OLED segments light up. When the Q5 starts to move, it returns to the original light signature. This is just an initial example of the automobile’s car-to-x communication with its surroundings. Subject to legislative approval, predefined warning symbols are conceivable in the future as well. The development and approval of the first dynamic turn signals is a good example of Audi’s effective engagement in collaborating with approval authorities. The developers present potential technologies and then adapt them as needed – which facilitates the homologation and approval of new ideas and concepts. Audi also shaped the developments around the digital OLEDs in advance in a way that made legislative approval possible for the Q5 in spite of differences in taillight design. Thus, the roads are becoming safer with lighting technology from Audi.
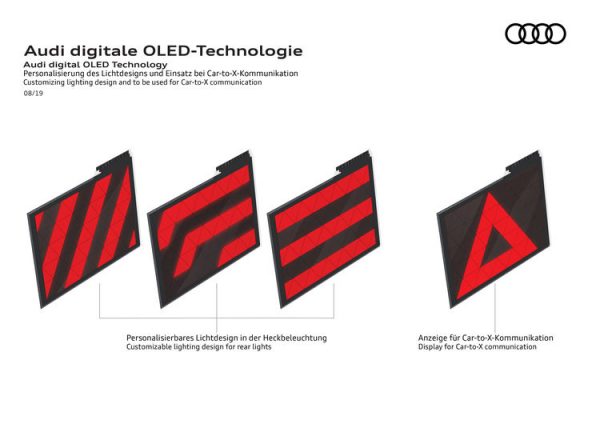
How will the development in this area continue?
Going forward, clearly more segments per taillight are conceivable, allowing for even greater personalization of signature lighting. For instance, predefined symbols might be displayed to provide other road users with early warnings of hazards such as slippery roads or the tail ends of traffic jams.



